728x90
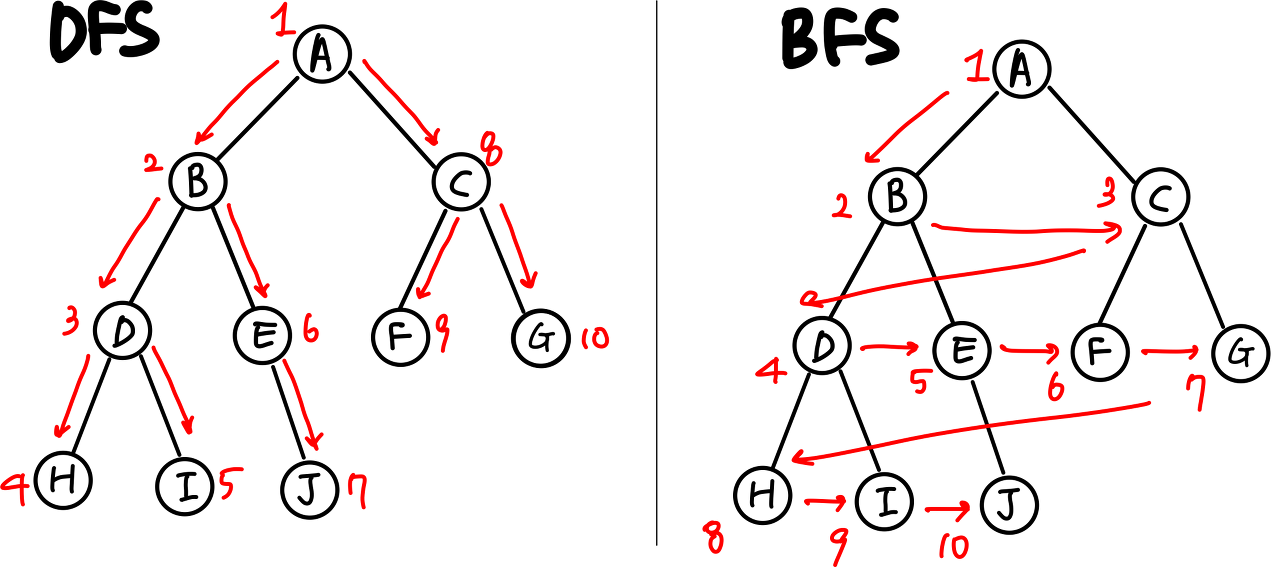
DFS & BFS
O(V^2) 또는 O(V+E)
dfs는 stack, bfs는 queue를 사용하는 것이 일반적이다.
시간복잡도는 입접 행렬로 구현하면 O(V^2), 입접 리스트로 구현하면 O(V+E)이다.
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260
1260번: DFS와 BFS
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000), 간선의 개수 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호 V가 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 간선이 연결하는 두 정점의 번호가 주어진다. 어떤 두 정점 사
www.acmicpc.net
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<Integer>[] list; // 인접 리스트
static boolean[] visited; // 방문 여부
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] input = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
int N = input[0], M = input[1], V = input[2]; // N: 정점의 개수, M: 간선의 개수, V: 탐색을 시작할 정점 번호
// 인접 리스트 초기화
list = new ArrayList[N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
list[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 연결 리스트 만들기
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
int[] uv = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
int u = uv[0], v = uv[1];
list[u].add(v);
list[v].add(u);
}
// dfs
visited = new boolean[N+1];
dfs(V);
System.out.println();
// bfs
visited = new boolean[N+1];
bfs(V);
System.out.println();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
static void dfs(int node) {
System.out.print(node+" ");
visited[node]=true;
ArrayList<Integer> nodes = list[node];
Collections.sort(nodes);
for(int al : nodes){
if(visited[al]) continue;
visited[al]=true;
dfs(al);
}
}
static void bfs(int node) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(node);
visited[node]=true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int nowNode = q.poll();
System.out.print(nowNode+" ");
ArrayList<Integer> n = list[nowNode];
Collections.sort(n);
for(int al : n){
if(visited[al]) continue;
visited[al]=true;
q.add(al);
}
}
}
}728x90
'algorithm > algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm] greedy (0) | 2023.02.09 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] binary search (0) | 2023.02.09 |
| [Algorithm] sliding window (0) | 2023.02.07 |
| [Algorithm] bubble sort (0) | 2023.02.07 |
| [Algorithm] two pointer (0) | 2023.02.07 |